Ever so slowly I'm creeping towards a description of my own research on the relation between braids and quantization. There are so many inviting byways...Anyway, recall where we were last time. (I never knew I'd become so professorial in my old age.)
Given an 1-1 and onto linear transformation
![]() , the Yang-Baxter equations say that
, the Yang-Baxter equations say that
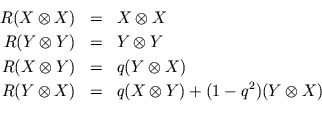
Quantum vector spaces were basically invented by Manin in his book, "Noncommutative Geometry and Quantum Groups," and I will only be talking about a subclass of his quantum vector spaces. To get at the concept, you have to think like an algebraic geometer -- or a quantum field theorist. To an algebraic geometer, what counts about a space is the algebra of functions on that space (to be a bit more precise, algebraic functions from that space to the complex numbers...and please, algebraic geometers, don't bother telling me how much I'm oversimplifying -- I know). To a field theorist, what counts about spacetime is the fields on spacetime, which are again functions from spacetime to the complex numbers. (And again, I'm vastly oversimplifying things.) There's a common theme here: for the algebraic geometer points may be regarded as secondary in importance to functions, while for the physicist particles may be regarded as secondary in importance to fields. This makes a lot of sense when you pay attention to what you're doing as you calculate: most of the time you are playing around with functions, and only at the end (if ever) do you bother to evaluate them at a given point.
Well, regardless of how true this actually is, it's a fruitful point of view! It gives rise to noncommutative geometry, in which points are not the point; rather, all attention is concentrated on the algebra of "functions on space," which is allowed to have a noncommutative product. Here I should mention Alain Connes, whose paper "Non-commutative differential geometry" really got the subject rolling in the early 1980's, though the notion of replacing functions on an honest space with a noncommutative algebra is as old as Heisenberg's matrix mechanics. In quantum mechanics, phase space disappears, but the analog of the functions on phase space, the algebra of observables (typically operators on a Hilbert space) lives on.
So now let us define our quantum vector space: what we'll really be defining is an abstract algebra, but in the back of our heads we'll always secretly pretend it consists of functions on some (nonexistent) space, a "quantum space."
First, notice that a Yang-Baxter operator ![]() on
on ![]() gives rise to a
Yang-Baxter operator
gives rise to a
Yang-Baxter operator ![]() on the dual space
on the dual space ![]() -- the inverse of the
adjoint of
-- the inverse of the
adjoint of ![]() . Recall that
. Recall that ![]() is none other than the linear functions on
is none other than the linear functions on
![]() . Normally we define the algebra of polynomial functions on
. Normally we define the algebra of polynomial functions on ![]() , or the
"symmetric algebra"
, or the
"symmetric algebra" ![]() , to be the quotient of the tensor algebra
, to be the quotient of the tensor algebra ![]() by the ideal generated by elements of the form
by the ideal generated by elements of the form
Now, all these duals and adjoints really just clutter things up a bit;
let's just define the r-symmetric algebra ![]() to be
to be ![]() modulo the
ideal generated by
modulo the
ideal generated by
The less jaded of you will be dazzled by the mere appearance of this bizarre entity. The more jaded will wonder what it's good for. Patience, patience. Let me just say for now that many papers have been written about this thing, in respectable physics journals, so it must be good for something. (?)
One can do all sorts of geometry on the quantum plane just as one does
on the good old classical plane. There is a "quantum group" of
"quantum matrices" which acts as linear transformations of the quantum
plane. One can differentiate and integrate functions on the quantum
plane, and so on. In fact, MIT just installed new blackboards in
some of the math classrooms which have a dial with which the instructor
can select the value of ![]() .
.
All but the last sentence of the previous paragraph is true. In fact,
the simplest quantum group, ![]() , consists of 2-by-2 "quantum
matrices" with "quantum determinant" equal to 1. It is a prototype for the
quantum groups
, consists of 2-by-2 "quantum
matrices" with "quantum determinant" equal to 1. It is a prototype for the
quantum groups ![]() . People are having a ball these days coming up
with
. People are having a ball these days coming up
with ![]() -analogs of everything they know about. For example, all
semisimple Lie groups admit quantizations of this general type, and such
quantum groups turn out to arise as symmetries of field theories in 2 or
3 dimensions (where anyonic statistics arise), and to be crucial for
understanding the HOMFLY polynomial and other knot invariants. I'm
running ahead of myself here and should quit and go to bed; next time
I'll either define quantum matrix algebras and
-analogs of everything they know about. For example, all
semisimple Lie groups admit quantizations of this general type, and such
quantum groups turn out to arise as symmetries of field theories in 2 or
3 dimensions (where anyonic statistics arise), and to be crucial for
understanding the HOMFLY polynomial and other knot invariants. I'm
running ahead of myself here and should quit and go to bed; next time
I'll either define quantum matrix algebras and ![]() , or start on what
I'm really interested in, the differential geometry of certain "quantum
spaces" (more precisely, algebras equipped with Yang-Baxter operators).
, or start on what
I'm really interested in, the differential geometry of certain "quantum
spaces" (more precisely, algebras equipped with Yang-Baxter operators).
© 1992 John Baez
baez@math.removethis.ucr.andthis.edu